Lyme Disease & Coinfections - Comprehensive Information and Expert Advice

Introduction
Welcome to "Jenny Demeaux, RNC ND" - your ultimate resource for information and guidance on lyme disease and its associated coinfections. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of lyme disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and expert advice on managing this complex condition. Gain a deeper understanding of lyme disease and empower yourself with the knowledge you need to overcome it.
Understanding Lyme Disease
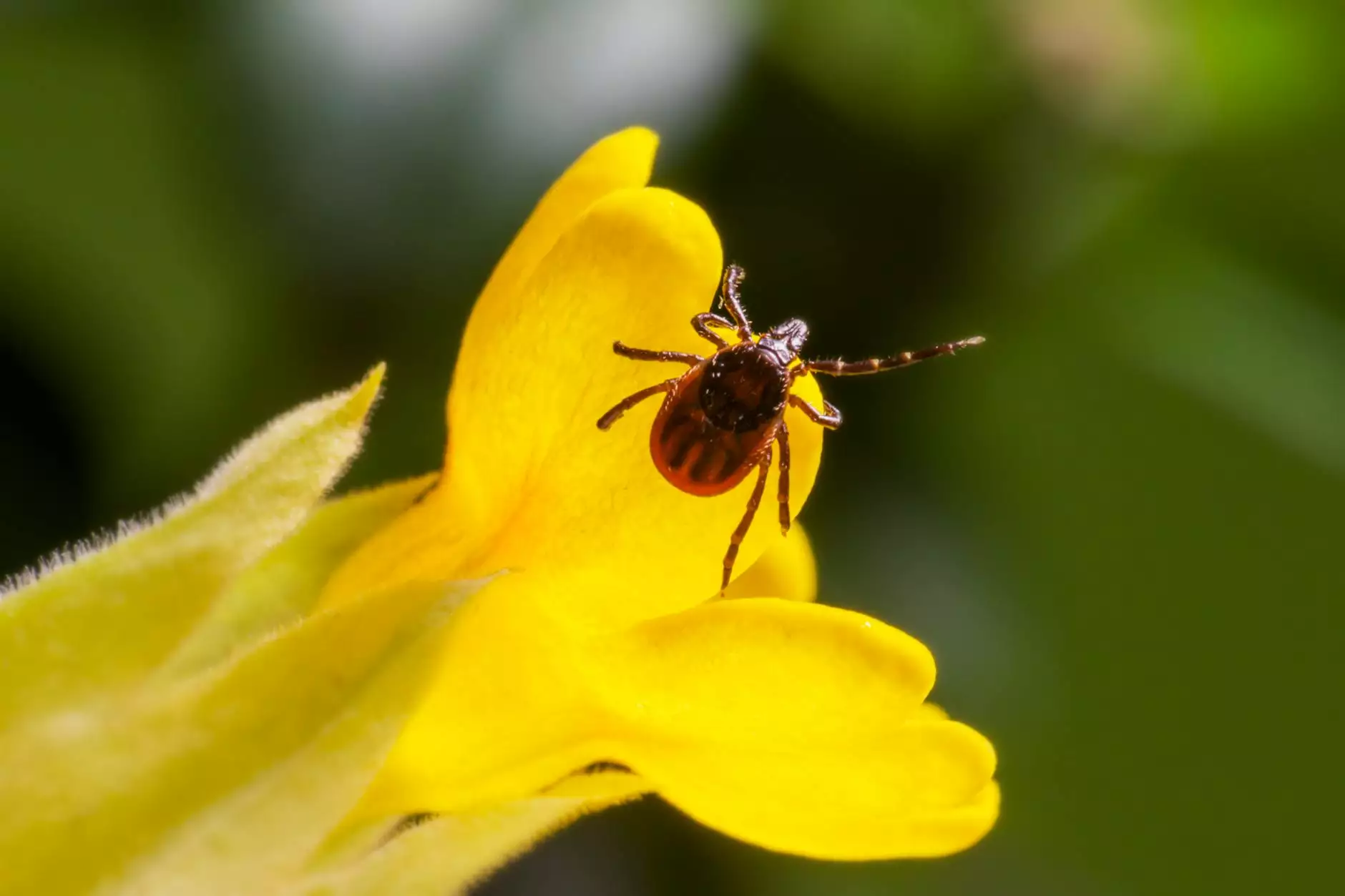
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. It primarily spreads through the bite of infected black-legged ticks and can affect multiple body systems, including the skin, joints, heart, and nervous system. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial for preventing severe complications.
Causes and Transmission
The primary cause of lyme disease is the bite of infected ticks, particularly the black-legged or deer tick. These ticks are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas, making outdoor activities the most common mode of transmission. It's important to note that not all tick bites result in lyme disease, as transmission depends on factors such as the duration of tick attachment and the presence of the bacterium in the tick itself.
Common Symptoms
Lyme disease manifests differently in individuals and can mimic various other conditions, making it challenging to diagnose. However, some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and flu-like symptoms
- Joint pain and swelling
- Headaches and migraines
- Rashes, including the characteristic bull's eye rash
- Cognitive difficulties and memory problems
- Nerve pain and tingling sensations
Diagnosis and Testing
Accurate diagnosis of lyme disease often requires a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and laboratory tests. While no single test is definitive, common diagnostic methods include:
- Antibody testing (ELISA and Western blot)
- PCR testing (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- Specialized tests for coinfections
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
Effective treatment of lyme disease involves a multidimensional approach that addresses both the infection and its accompanying coinfections. Here at "Jenny Demeaux, RNC ND," we advocate for a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to each individual's needs.
Antimicrobial Therapy
The cornerstone of lyme disease treatment is antimicrobial therapy, which aims to eradicate the bacterium causing the infection. This can include the use of antibiotics or natural antimicrobial agents to target the various forms of the bacterium.
Supportive Treatments
In addition to antimicrobial therapy, supporting the body's overall health and immune system is essential. This may involve addressing nutritional deficiencies, reducing inflammation, managing stress, and strengthening the body's natural defenses.
Coinfection Management
Lyme disease often comes hand-in-hand with various coinfections, such as Babesia, Bartonella, and Mycoplasma. Effective management of these coinfections is vital for successful recovery. Our expert advice and comprehensive treatment protocols can help address each specific coinfection with precision.
Expert Advice and Support
At "Jenny Demeaux, RNC ND," we understand the complexities and challenges of living with lyme disease. Our priority is to provide you with expert advice, support, and guidance throughout your journey. Whether you're in the early stages of diagnosis or seeking alternative treatment options, we are here to empower you with the knowledge you need to overcome lyme disease and regain your quality of life.
Conclusion
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of lyme disease, its coinfections, and the various treatment approaches, take the first step towards a healthier future. Explore our website further for more resources, treatment options, and expert advice. With "Jenny Demeaux, RNC ND," you have a trusted partner by your side in your battle against lyme disease and its associated coinfections.